Human Metapneumovirus, or HMPV virus, is believed to be one of the most viral respiratory viruses of the 21st century, infecting millions from every corner of the globe. It was first discovered in 2001 by scientists from Erasmus Medical Centre located in the Netherlands, this virus has redefined how one perceives respiratory infections along with its consequences to public health. It was an astonishing find since it showed that for the first time, there existed a virus that was responsible for respiratory infections in humans, but for some unknown reason, remained undetected for centuries.
The HMPV virus does not only cause human distress but is responsible for the greatest reverse economic impact on modern healthcare systems, as millions of dollars are spent every year, due to it, for example, over 100k children are hospitalized every year as a consequence of HMPV, the numbers being significantly greater during the seasonal peaks of respiratory viruses. HMPV is actively being investigated and studied as it has an alarming potential to inflict high populations suffering from previously existing medical conditions. Understanding HMPV, an acute disease, has grown exceedingly important over the recent years as more and more people face serious consequences along with the aforementioned viruses.
 This in-depth article will specifically analyze the HMPV virus in great detail ranging from its defining traits to the singular medicine that can stop it, aiming to target both medical professionals and the masses equally.
This in-depth article will specifically analyze the HMPV virus in great detail ranging from its defining traits to the singular medicine that can stop it, aiming to target both medical professionals and the masses equally.
What is HMPV Virus?
The Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a virus that infects or targets the human respiratory system and is categorized as a member of the family of Pneumoviridae. Membranes of lipids surround its genome, which is composed of single-stranded RNA and is negative sense. HMPV virus, as well as RSV, are biologically similar, and function, transmit, and also mutate similarly. Just like RSV, HMPV was actually identified not long ago in the medical field but has been affecting the human population around the globe for many years now.
This particular HMPV virus comprises various important viral proteins that are crucial for HMPV functions. The virus’s structure consists of a negative-sense single-stranded RNA genome, encased in a lipid envelope. This structure is crucial for understanding its behavior and developing targeted treatments. The virus contains several important proteins that play key roles in its ability to infect and spread, including:
- Fusion (F) protein: Enables the virus to enter host cells
- Glycoprotein (G): Helps in attachment to host cells
- Small hydrophobic (SH) protein: Assists in viral replication
- Nucleoprotein (N): Protects the viral genome
According to a study, the HMPV Virus affects approximately 5-10 percent of the entire global population of children and adults bringing the number of infections to millions every year during late winter and early spring as this is when HMPV virus reaches its peak.
How HMPV Virus Spreads
HMPV virus is most communicable as a result of a variety of ways it can be transferred and the ways of transfer are in plenty. It is crucial in the prevention of transmission of the HPV virus that these routes are known so let’s read how HMPV virus is transmitted:
Primary Transmission Methods:
-
Respiratory Droplet Transmission:
- When a person coughs, speaks, or sneezes, they release droplets that can infect others. Droplets can travel approximately up to a distance of six feet.
- People with the highest risks are in multidimensional poorly ventilated rooms. Under some circumstances, droplets may stay in the atmosphere for hours.
-
Surface Contamination:
When a person interacts physically with common surfaces the virus can remain active for up to a couple of days. Common surfaces where an individual can get contaminated include:
- Doorknobs and light switches
- Shared electronic devices or appliances
- Countertops, tables around the house
- Childcare materials, toys, and educational materials for kids, etc.
HMPV Transmission occurs when people touch the contaminated surfaces and then touch their face, eye, nose, or mouth.
-
Direct Contact:
- Sharing items, belonging to an infected person
- Close physical contact during care of infected persons such as touch or handshake
- Handling contaminated materials without protective measures
Transmission Dynamics of HMPV Virus:
It is demonstrated that HMPV virus has certain differences in its mode of transmission in varied environments:
1. Household Settings:
-
- High transmission rates among family members especially elderly and children
- Longer household visits raise the chances of an infection
- Children frequently act as the first carriers
2. Healthcare Settings:
-
- A possibility of viral transmission in hospitals
- Workers in the health sector can also act as carriers of infection
- Correct use of medical protective equipment is essential
3. Community Settings:
-
- Primary places of infection include schools and childcare centers
- Public transportation can facilitate the spread of the infection
- Seasonal variations affect transmission rates
For example, infection with the HMPV virus in a typical household setting, when one of the residents develops the illness, 70%-80% of other residents tend to get infected within 2 to five days, this tendency of rapidly increasing infection rate is also evident in common cold viruses making it extremely difficult to control the HMPV virus within a household after its introduction.
HMPV Virus Symptoms
HMPV is characterized as a respiratory-related disease and displays various signs that manifest in different severities throughout the age and health status of an individual, this virus especially targets a certain group of people, including infants less than 6 months of age, people more than 65 years and people with different immunocompromised states or those with compromised immune system.
Studies indicate that the intensity and length of HMPV virus symptoms are affected by things like existing breathing problems overall wellness, and quick medical help. Also, the virus follows seasonal trends, with symptoms getting worse in winter when our immune systems might already be struggling with other breathing infections. Here’s a full breakdown of HMPV Virus symptoms and how they progress:
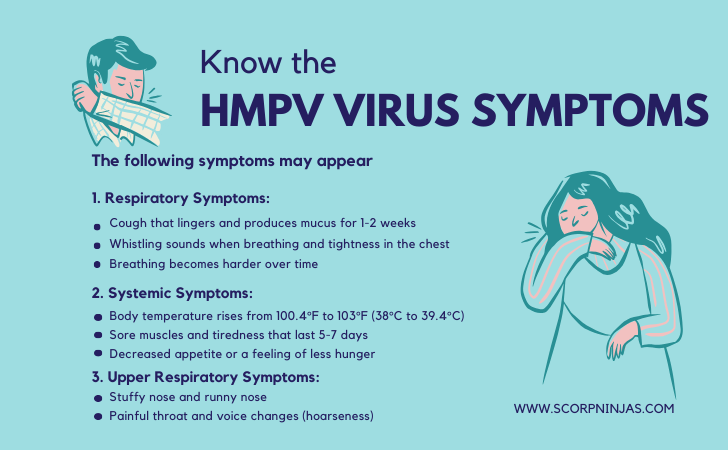
Primary Symptoms of HMPV Virus
The main symptoms of HMPV virus show up 3-6 days after exposure and can change in strength throughout the illness. These symptoms often start and might seem like a regular cold at first, but they tend to get worse faster and can be more serious for certain people. The key symptoms of HMPV virus fall into three main groups:
1. Respiratory Symptoms:
-
- Cough that lingers and produces mucus for 1-2 weeks
- Whistling sounds when breathing and tightness in the chest
- Breathing becomes harder over time
Example: A kid may begin with a slight cough that gets more common and sounds wet as days go by.
2. Systemic Symptoms:
-
- Human body temperature/ fever rises from 100.4°F to 103°F (38°C to 39.4°C)
- Sore muscles and tiredness that last 5-7 days
- General malaise and decreased appetite or a feeling of less hunger
Example: An adult might get fever peaks at night, accompanied by severe body aches.
3. Upper Respiratory Symptoms:
-
- Stuffy nose and runny nose
- Painful throat and voice changes (hoarseness)
- Sinus pressure and headaches
Example: It’s like a bad or severe cold, but it often lasts longer.
So if you or anyone you know have similar symptoms listed above, we advise you to consult a doctor as soon as possible. Now that you are more aware of the symptoms of HMPV virus let’s continue further about the complications of HMPV virus in people at high risk.
Severe Complications of HMPV
HMPV virus in people at high risk can cause:
- Bronchitis:
-
- Heavy chest congestion
- Long-lasting cough fits
- Chest pain and discomfort
- Pneumonia:
- Trouble breathing while resting Chest
- Severe Chest pain during breathing
- Potential need for hospitalization
- Groups at Special Risk:
- Older people: More likely to have bad breathing problems
- Children: Higher chance of wheezing and bronchiolitis
- People with weak immune systems: Might get life-threatening issues or situation
Diagnosis and Treatment of HMPV Virus
To identify HMPV, doctors need a mix of medical know-how, lab tests, and a close look at the patient. Medical professionals use several tools and methods to confirm if someone has HMPV and to tell it apart from other breathing problems like the flu or RSV. It’s essential to spot HMPV virus to plan the right treatment and stop things from getting worse, especially for people who are at high risk.
Diagnostic Approaches
- Laboratory Testing:
- PCR testing of nasopharyngeal swabs – Doctors consider this the best way to detect HMPV Virus
- Rapid antigen detection tests – Give results within a few hours
- Blood tests to check for signs of inflammation
Example: A doctor might ask for both PCR and blood tests to tell HMPV apart from other breathing problems
- Clinical Assessment:
- Detailed physical examination, including checking and monitoring vital signs
- Listening to the lungs to spot unusual breathing patterns
- Checking oxygen levels with a pulse oximeter
Example: Healthcare providers listen for distinctive breathing sounds that indicate lower respiratory involvement
- Medical History Evaluation:
- Asking about recent exposures, trips, or travel records
- Checking for health issues (pre-existing conditions) that could make treatment tricky
- Looking at current medications to avoid bad reactions
- Documentation of allergies and past breathing problems or respiratory infections
In addition to these primary diagnostic methods, Doctors may also think about these other ways to diagnose:
- X-rays of the chest when doctors think a patient might have pneumonia
- CT scans for patients with severe cases or other respiratory-related problems
- Bronchoscopy for some specific complicated cases
- Tests on sputum to check if bacteria are also causing trouble
Also Read: Somatic Healing: A New Path to Trauma Healing
Comprehensive Treatment Plan for HMPV Virus
The treatment of HMPV virus infection can vary from person to person depending upon the symptoms that he or she is facing at the current time. Here are some fundamental measures that should be followed to fight HMPV:
- Supportive Care:
- Rest: at least 7-10 days of reduced physical activity.
- Hydration: 8-10 glasses of water every day.
- Humidification: Maintain humidity within the range of 40 giving 60 percent Example: Use a humidifier at night while sleeping. This greatly eases respiratory symptoms.
- Medication Management:
- Over-the-counter medications:
- Acetaminophen or ibuprofen for fever
- Decongestants for nasal symptoms
- Night-time cough suppressant for relief
- Prescription medications (in severe cases):
- Bronchodilators
- Corticosteroids
- Antiviral medications in specific cases
- Over-the-counter medications:
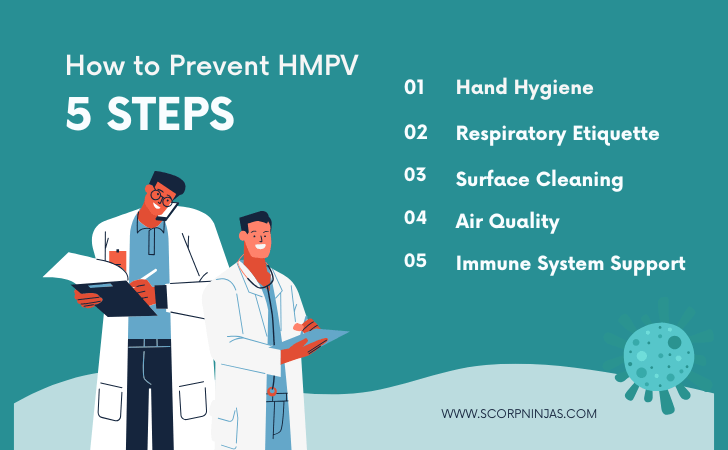
How to Prevent HMPV / Prevention Strategies
There are quite a few practices essential to prevent HMPV virus from spreading and affecting other individuals. They are:
Personal Hygiene:
- Hand Hygiene:
- 20 seconds of handwashing with soap or liquid handwash
- Constant use of alcohol-based sanitizers Example: Hands should be washed before meals, after using restrooms, and after touching public surfaces.
- Respiratory Etiquette:
-
- When in high-risk settings (crowded places), wear a mask appropriately
- Cover mouth when coughing/sneezing
- Proper disposal of tissues
Environmental Measures:
- Surface Cleaning:
-
- Daily disinfection of frequently touched surfaces
- Use of EPA-registered disinfectants Example: Wiping down doorknobs, light switches, and electronic devices daily
- Air Quality:
-
- Proper ventilation
- Routine changes of air filters
- Optimal humidity levels and maintaining it
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Immune System Support:
-
- A balanced diet with lots of vitamins C and D
- Working out / Yoga (30 minutes each day)
- Enough sleep (7-9 hours) Example: Eating oranges and leafy greens like spinach and spending time outside daily
Conclusion
To wrap up, HMPV is a virus that affects breathing and can lead to different symptoms in people who are more likely to get sick. Knowing what is HMPV virus, its symptoms, how HMPV virus spreads, and ways to avoid it helps you stay informed and protect yourself and others. If you or someone you know feels sick, it’s crucial to see a doctor to get checked out and treated. Keep yourself safe and up to date on HMPV and how the HMPV virus affects your breathing health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About HMPV
How long does HMPV infection last, and when should I seek medical attention?
HMPV infections stick around for 7-14 days. Get medical help right away if you have trouble breathing, a high fever that won’t go down (over 103°F/39.4°C), or if you start feeling worse after you thought you were getting better. People who are at high risk should talk to their doctor as soon as they think they might be sick.
Can someone get infected with the HMPV virus multiple times, and is there a vaccine available?
Yes, HMPV virus can infect people more than once because the virus has different strains, and immunity doesn’t last long. Right now, no approved vaccine exists for HMPV, which makes it essential to prevent infection by following or practicing good hygiene. Researchers are busy working on possible vaccine options.
What sets HMPV apart from other respiratory viruses like the common cold or flu?
HMPV shares symptoms with other breathing infections, but it often has a more serious effect on the lower respiratory system in people at risk. The virus takes longer to show up (3-6 days) than regular colds, and signs come on but can stick around. Unlike the flu, we don’t have specific drugs to treat HMPV.
What’s the relationship between HMPV and asthma or other respiratory conditions?
HMPV has an impact on asthma flare-ups and can make existing breathing problems worse. People with long-term breathing issues should:
- Keep taking their prescribed meds as usual
- Have a plan ready for when symptoms get worse
- Reach out to their doctors if HMPV symptoms show up
How does HMPV affect pregnant women and their unborn babies?
Pregnant women need to be extra careful because they might get sicker from HMPV due to normal changes in their immune system during pregnancy. While it’s not common for the virus to pass to the baby or the fetus, severe respiratory infections can affect oxygen levels, making early medical consultation important.
Also Read: 10 Surprising Benefits of Jaggery for Skin and Health